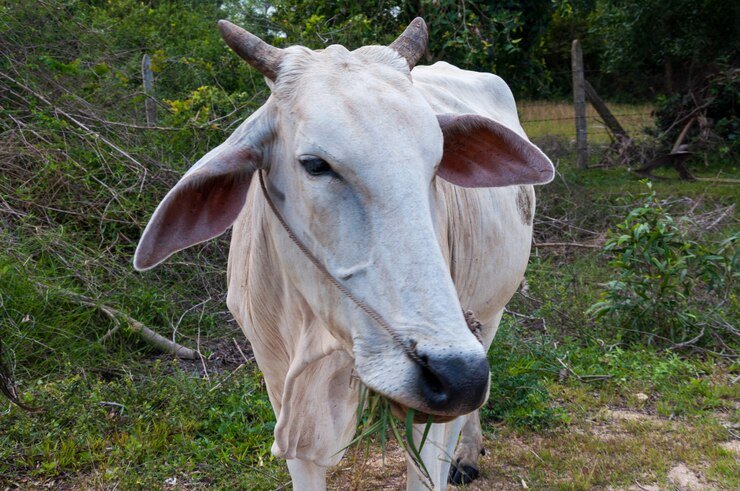
Gir
One of the most well-known dairy breeds in India is the Gir cow, which comes from the Gir forest area of Gujarat. Gir cows are distinguished by their long, drooping ears and domed forehead. They are also resistant to common diseases and can withstand tropical conditions. The high milk yield of this breed—12 liters on average per day, with some cows producing up to 25 liters—makes it particularly well-known. Because of its high fat content, the milk is perfect for manufacturing ghee and other dairy products. In addition to increasing milk output in India, gir cows have been successfully transferred to other nations, like as Brazil, where they flourish and support regional dairies.
Sahiwal
Sahiwal cows, one of the best dairy breeds in India, are native to Punjab's Sahiwal area, which is now in Pakistan. They are a popular breed in the tropical areas of India and its adjacent nations because of their high milk supply and ability to withstand heat. Compared to many other breeds, Sahiwal cows typically produce 8–10 liters of milk per day with a butterfat percentage of 4.5%. This breed is extremely significant, particularly in arid regions, because it can produce high-quality milk while using less water.
Red Sindhi
Red Sindhi cows are famous for their rich red color and capacity to adapt to a variety of environmental circumstances. They are native to Pakistan's Sindh area. These cows produce about 8 liters of milk a day, which is considered medium, but the milk has a really high butterfat percentage (about 5% on average). Because of this, it is ideal for making cheese and butter. The durability and production of Red Sindhi cows make them valuable not only in India but also in Southeast Asia and other tropical regions.
Tharparkar
Named for the Thar Desert in Rajasthan, India, Tharparkar cows are known for their remarkable ability to adapt to arid and harsh environments. These medium-sized, white or light gray cows are renowned for their ability to persevere and produce quality milk even in the face of adversity. The milk produced by a Tharparkar cow, which is prized for its great quality, usually amounts to 6-8 liters per day. The breed is essential to maintaining the rural economy in arid regions since it produces milk, which is a reliable source of income.
Rathi
The dry areas of Rajasthan, especially Bikaner, Jodhpur, and Jaisalmer, are the birthplaces of Rathi cows. By crossing local cattle with breeds like Sahiwal and Red Sindhi, this breed has the greatest traits of both. With a daily average yield of 6-7 liters of milk, Rathis are renowned for producing high-quality milk with a 4-5% butterfat percentage. The local dairy farming communities rely heavily on them, and they thrive in Rajasthan's hot, dry climate.
Kankrej
One of India's oldest and most prestigious cow breeds is the Kankrej, which comes from the Gujarati Kankrej region. Kankrej cows, distinguished by their characteristic big hump and long, sweeping horns, are prized for their great milk yield and draw ability. Because of their ability to withstand high temperatures, these cows are perfect for the dry regions of Gujarat and Rajasthan. Approximately 6–8 liters of milk can be produced daily by a Kankrej cow, with some exceptional animals producing up to 10 liters. The milk is valued for its high quality and suitable fat content for making butter and ghee. Additionally, the breed supports many farming households in rural India, contributing significantly to the socioeconomic fabric of the area.
Ongole
The Ongole breed from Andhra Pradesh is famed for its robustness and strength. Derived from the Nellore breed, these cows are primarily draught animals but also known for their milking potential. Ongole cows are large with a well-built frame and white or gray coat. They are capable of producing 6-8 liters of milk per day under optimal conditions. The breed's hardiness makes it popular not just in India but also in other tropical countries where they are exported to improve local cattle genetics. Ongole cows are a symbol of strength and endurance in Indian cattle culture, contributing significantly to agricultural operations.
Deoni
The Deoni breed, which originated near the junction of Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Telangana, is easily identified by its characteristic three-color pattern, which is usually black, white, and red. This particular breed is renowned for its ability to be used for both milking and draught. Deoni cows, which yield roughly 4-5 liters of milk each day, are prized for their ability to adapt to the semi-arid areas of central India. The breed is an essential resource for the area's smallholder farmers, helping them with field work and dairy requirements because to its adaptability and moderate milk production.
Hariana
Originating in the Haryana region, the Hariana breed is widely distributed in Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, and portions of Madhya Pradesh. Although they are mostly used for draught, Hariana cows, who are distinguished by their huge frame and robust body, also produce a respectable amount of milk. The average Hariana cow yields 5–6 liters of high-quality milk each day. They are an essential component of North India's agricultural environment because of their capacity to work hard in challenging weather circumstances and provide the farmer's dairy needs.
Krishna Valley
Krishna Valley cows, so named because of the valley where the Krishna River flows, are well-known in Maharashtra, Karnataka, and some areas of Andhra Pradesh. These huge, strong cows are well-suited to the harsh circumstances found on the peninsular plateau. They produce about 6-7 liters of milk every day, while some cows produce considerably more. Crucial to the livelihoods of the local farming community, the breed is prized for both its milk and its resilience in the harsh, arid environment of its home region.